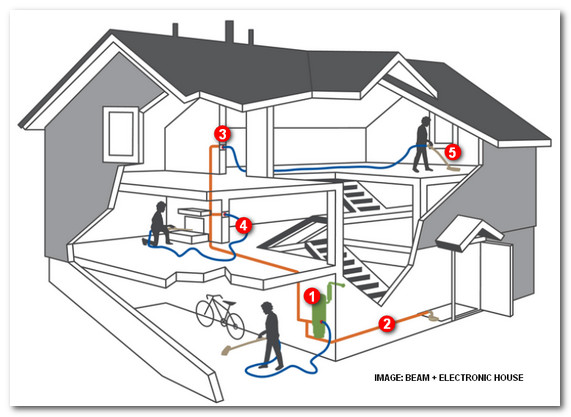
What goes into a central vacuum system? We lay out the five basic pieces: power unit, piping, inlets, hoses and brushes and accessories.
Do you hate dirt and hate to vacuum? A central vacuum system may be just what you need. Instead of lugging a canister around the home, the heavy lifting is done by a power unit located some place like the garage, where it can barely be heard.
A central vacuum system can also be a healthier and greener choice, as it won’t emit dirt particles into the air, as do some other vacuum systems.
For consumers who are new to the category, we provide the foundations of a central vacuum system.
1. Power Unit
Drives the system and is usually mounted in the garage.
Bag vs. cyclonic (bagless) filtering: Bag-type systems require users to replace bags, but don’t require venting the system to the outdoors. Cyclonic units require no messy bags, but do need to be exhausted to the outdoors. Typical homes under 6,000 square feet can run off of a dedicated 20-amp, 120-volt circuit. Larger homes may require a larger, dedicated circuit. AirWatts typically indicate the power of the unit, but be cautious of using single high-air watt motors in larger home applications, as they may wear out too soon. Consider a unit with a utility valve on the tank for cleaning the cars and garage Typically code requires the wall between the garage and home to be penetrated with steel pipe. Check local building codes for safety requirements.
2. Piping
Provides suction from the power unit and delivers waste to the power unit.
2-inch special piping tested to specific standards. Cut the pipe with a miter box, chop saw, or tubing cutter. It must have a smooth, straight cut to reduce potential for debris getting stuck. Use wide sweeping turns at all locations after the inlet valve. For less friction loss, make jogs with 45-degree ells instead of 90-degree ells. Low-voltage wire follows along the outside of the pipe. Strap it to the pipe with zip ties or tape. Wire is run in series rather than home-run.
3. Inlets
Installed in the walls between piping and hoses.
Typically, one inlet covers 600 to 900 square feet of living space. Inlets are located at the same height as electrical outlets, but they can also fit in to the baseboards. Inlets are available as “air-only” or electrified. Electricity is required for traditional power brushes, but can still be provided with a separate cord for non-electrified (less expensive) outlets. Remember to place inlets near outdoor patios and porches. Plan for an inlet near the base of the stairs.
4. Hoses
Connect from the inlet to the vacuum cleaner.
Hoses normally come in 30-foot lengths, but 35-footers are available. Consider buying an additional hose and tool set for upstairs. A hose sock can protect baseboards and furniture. Designate a closet to hang the hose and tool set. Options are available for easy-to-tote spools and for hoses (up to 50 feet) that retract into walls.
5. Power Brushes, Accessories
Connect to hoses for cleaning everything from carpeting to pets.
Power brushes are the best central vac accessory for cleaning carpets and other flooring. Most brushes require electricity, but some lower-powered units can operate via air power. Brushes come in a variety of shapes and sizes for cleaning upholstery, staircases, cars, underneath furniture and more. Additional accessories can be used for cleaning tight spaces, ceiling fans, pets and more.
Grant Olewire of MD Manufacturing contributed to this article.
By CE Pro Editors
http://www.cepro.com/article/anatomy_of_central_vac_systems/T320